What is the Bitcoin Genesis Block? This is what you need to know!
2024-07-12
Bittime - Genesis block is one of the most fundamental in blockchain. So, this article will discuss what the Bitcoin genesis block is, why it is important, and how it functions in the blockchain world.
What is Genesis Block Bitcoin?
A genesis block, literally meaning “initial block”, is the first block created on a blockchain network. It is like a solid foundation stone, anchoring the pillars for all subsequent blocks that will be added in the future.
In a proof-of-work (PoW) system like Bitcoin, the genesis block is the first block ever mined. It became the foundation for all blocks that followed. Typically, genesis blocks are created by the blockchain creator himself and “programmed” into his network protocol.
Traditional mining processes do not apply to genesis blocks because there are no previous blocks that can be used as a reference.
Meanwhile, in a proof-of-stake (PoS) network, the genesis block is usually created by the developer or network validator who starts the process. The selection of validators may be based on certain criteria listed in the protocol.
This is done instead of going through the staking process, considering that there are no transactions or stakes that can be used as a reference.
The Story of the Birth of the Bitcoin Genesis Block
The concept of the genesis block was born at the same time as the launch of the Bitcoin network in 2009. The pseudonymous figure of Bitcoin's creator, Satoshi Nakamoto, created the first block on the blockchain chain which later became the most valuable crypto asset in the world with the highest market capitalization.
Interestingly, Bitcoin's capitalization even surpassed that of silver for a short time. This genesis block marks the important role of initial blocks in launching a decentralized and well-functioning blockchain ledger.
Check Today's Crypto Market:
Genesis Block Bitcoin Core Purpose
The main purpose of a genesis block is to initiate a blockchain by cryptographically connecting to subsequent blocks. It is the starting point that becomes the anchor for the blockchain, as well as building trust in the immutable ledger.
The genesis block also sets initial parameters. Examples include mining difficulty and block rewards, which govern the network's operations and incentive structure. Without the foundation provided by the genesis block, the blockchain would not have a secure and trustworthy foundation to build on.
All crypto networks require a genesis block to start their ledger. For example, Ethereum's genesis block contains instructions for initial Ether (ETH) allocation and core network parameters.
The genesis block provides a solid starting point, on which ever-evolving blockchains can be built. Without a genesis block, a blockchain would have no foundation for permanently recording transactions via cryptographic hashes.
Genesis Block in Bitcoin
Satoshi Nakamoto pioneered the use of the genesis block to launch the Bitcoin blockchain. He helped establish various technical attributes and issuance models that are still followed by many cryptocurrencies today.
Bitcoin's genesis block was mined on January 3, 2009, and is known as block 0. This block was created by Satoshi Nakamoto as the first step to launching the network and starting the first crypto asset.
Nakamoto designed Bitcoin's genesis block to define the core technical elements of the protocol and set certain launch parameters. The block contains a reference to a headline, "The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks," published in the London newspaper, The Times, on January 3, 2009.
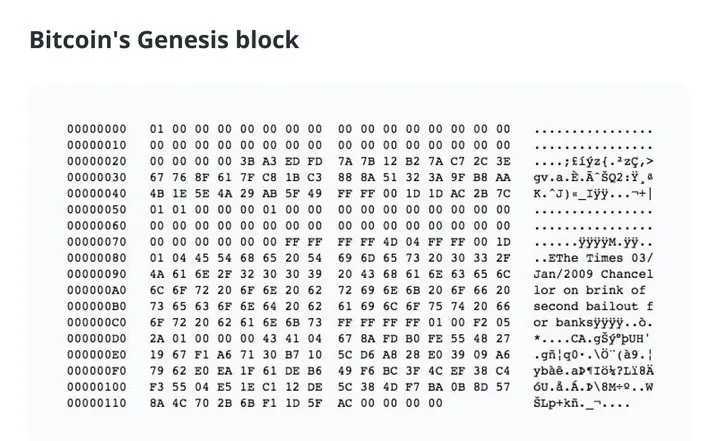
By including these headlines, Nakamoto timestamps the blocks and provides poetic context for Bitcoin's mission as a decentralized alternative to traditional financial systems.
The "nonce" field in the genesis block has a special value, namely 2083236893. This number was discovered by Satoshi Nakamoto through a mining process to meet the target difficulty at the time of the launch of the Bitcoin network.
Even though the difficulty level at that time was much lower compared to today's standards, creating a genesis block still required adjusting the nonce value. So, a valid block hash can be found that meets the target.
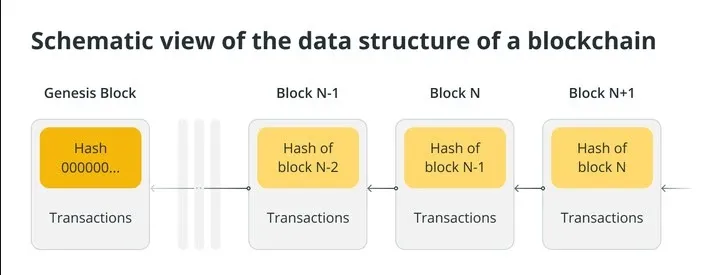
All subsequent blocks are built on the genesis block's hash, creating a chain that connects each block to the origin block.
One of Nakamoto's most important decisions was setting the mining reward for adding new blocks to the blockchain. The Bitcoin genesis block contains a coinbase transaction that awards 50 Bitcoins (BTC), while establishing a Bitcoin issuance model.
However, these special rewards cannot be spent due to the unique way genesis blocks are “programmed” into the Bitcoin software.
This 50 BTC reward sets the precedent for subsequent block rewards, which will be halved approximately every four years until a total supply of 21 million is reached.
Bitcoin's "programmed" genesis block design it establishes Bitcoin's core technical and monetary attributes. As the first block on the Bitcoin blockchain, the genesis block enabled the launch of the network's distributed ledger, paving the way for innovation in blockchain technology, crypto assets, and the world of finance.
Genesis Block in Other Crypto Assets
Although Bitcoin pioneered the use of genesis blocks, other crypto assets have adapted this mechanism to launch their own blockchain networks.
The Ethereum genesis block was mined in 2015 as the foundation for the Ethereum blockchain. This block establishes the initial supply and distribution of ETH tokens by allocating the Ether purchased by early users during the pre-sale.
However, the genesis block itself does not implement the network's PoW consensus model. This was a separate part of the Ethereum protocol design (before the Merge).
Ethereum's approach differs from Bitcoin in several ways. Most notably, in the initial token distribution method, which allows early users to purchase ETH, Ethereum's native crypto asset, before the network launches.
Many crypto assets follow Bitcoin's genesis block format closely at launch. Litecoin's 2011 genesis block mirrored Bitcoin's, with minor changes to technical parameters such as mining algorithms.
Dogecoin's genesis block in 2013 paid homage to Bitcoin's genesis block. This first encrypted block of Dogecoin refers to newspaper headlines about Bitcoin's increasing value.
Some differences can be seen when comparing the genesis block of crypto assets. Some display a timestamp in the past as a proof-of-work time stamp, while others timestamp the genesis block more recently.
Initial mining difficulty and block reward amounts also vary between crypto asset genesis blocks.
Despite their similar structure, each genesis block is unique in initializing the blockchain's distributed ledger. The blockchain industry continues to innovate the genesis block structure with alternatives such as proof-of-stake consensus models.
However, the genesis block still has an important symbolic role, representing the beginnings of a transparent and decentralized financial system.
Also Read How To Buy Crypto:
Genesis Block Components and Structure
The genesis block lays the foundation for the blockchain by establishing the format for data and structure that all subsequent blocks will follow.
The genesis block contains the fundamental data that forms the foundation for the rest of the blockchain. This starter block is "programmed" with index 0 and sets the structure that subsequent blocks will follow.
Data embedded in the genesis block includes timestamp, block hash, previous block hash, nonce, and block reward address. The timestamp indicates when the block was created, while the hash of the previous block is a string of zeros because no previous block exists.
In a PoW blockchain like Bitcoin, the nonce is a value that is varied to find a valid block hash that meets the network difficulty target. However, the significance and use of nonces may vary across different blockchain implementations, especially those that do not use PoW consensus.
The block reward address indicates where the block reward should be sent, although its function is different in the genesis block compared to subsequent blocks.
It is worth noting that the concept of block reward addresses is more nuanced in genesis blocks, as they do not function in the traditional sense as seen in later blocks, especially in a network like Bitcoin, where genesis block rewards cannot be spent.
Events After the Genesis Block
Genesis block launches the network. Then, confirmations, incentives, and difficulty adjustments enable decentralized propagation, consensus, and mining to develop the blockchain.
Once the genesis block is created, the blockchain network can be officially launched. This milestone opens up public participation and begins the process of consensus and decentralization.
After launch, the blockchain starts building on top of the genesis block. As a prime block, a genesis block is automatically accepted as valid by network nodes.
But this block does not require confirmation in the traditional sense as is done in next transaction or block. Subsequent blocks refer to the genesis block hash, building an unbroken chain that connects back to the starting point of the network.
With the confirmation of the genesis block, miners begin to compete to add new blocks. As new blocks are added, confirmations for previous blocks accumulate, strengthening the immutability of the blockchain. New coins are issued via block rewards, and transactions are validated.
The network difficulty dynamically adjusts based on activity to maintain a block creation rhythm. More miners and high participation increase competition and difficulty, while lower activity lowers the target difficulty. These fluctuations ensure blockchain self-regulation.
After block genesis, the blockchain grows organically through decentralized propagation, consensus mechanisms, and incentivized mining. This activity strengthens the genesis block as an unshakable anchor point. Transactions are growing rapidly as adoption expands.
In the case of crypto asset blockchains, value increases with trust in the network. Coins gain monetary value according to market dynamics of supply and demand. Real-world speculation, trading, and utility drive investment and participation.
The genesis block also switches from its honorary role when the network is active. The launch it facilitated gave birth to a bustling ecosystem governed by participants aligned with economic interests through blockchain incentive structures.
Conclusion
The genesis block is a vital foundation block for the blockchain. It plays an important role in launching the network, setting initial parameters, and connecting all subsequent blocks. The genesis block became a symbol of the beginnings of an innovative and decentralized financial system.
An understanding of block genesis is essential for anyone interested in blockchain technology and crypto assets. Bitcoin's genesis block is a reminder of the power of decentralization and the revolutionary potential of blockchain technology.
How To Buy Crypto With Bittime
You can buy and sell crypto assets in an easy and safe way via Bittime. Bittime is one of the best crypto applications in Indonesia which is officially registered with Bappebti.
To be able to buy crypto assets on Bittime, make sure you have registered and completed identity verification. Apart from that, also make sure that you have sufficient balance by depositing some funds into your wallet. For your information, the minimum purchase of assets on Bittime is IDR 10,000. After that, you can purchase crypto assets in the application.
Learn How to Buy Crypto on Bittime.
Monitor price chart movements of Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), Solana (SOL) and other cryptos to find out today's crypto market trends in real-time on Bittime.
Disclaimer: The views expressed belong exclusively to the author and do not reflect the views of this platform. This platform and its affiliates disclaim any responsibility for the accuracy or suitability of the information provided. It is for informational purposes only and not intended as financial or investment advice.