ROE is: Definition, Examples, and Differences with ROIC
2024-08-12
Bittime - The world of finance and investment has many metrics that are used to evaluate company performance. One of the most common metrics used by investors and analysts is Return on Equity (ROE).
ROE is a reflection of how effectively a company manages the capital invested by shareholders to generate profits.
So, this article will dig deeper into what ROE is, how to calculate it, examples of its use, and how it differs from Return on Invested Capital (ROIC). So, you can get a clearer picture in assessing a company's financial performance.
What is ROE?
ROE is a financial ratio used to measure a company's ability to generate profits from each unit of shareholder equity invested.
In simpler terms, ROE shows how much profit a company generates from the capital provided by shareholders. This can be calculated after deducting all debts.
The higher the ROE, the more efficient company management is in using equity to generate profits.
How Does ROE Work?
ROE is expressed in percentage form and can be calculated for any company as long as its net income and equity are positive. Net profit is obtained after deducting all costs.
This includes interest and taxes, as well as before dividends are paid to shareholders. Shareholders' equity is the difference between the company's total assets and its total debts.
ROE is often compared to the average ROE of other companies in the same industry. It is used to assess whether a company's performance is above, below, or in line with industry standards.
For example, in the utilities sector, which typically has a lot of assets and debt, a normal ROE might be around 10% or less. Meanwhile in the technology sector, ROE can be higher, reaching 18% or more.
A common benchmark that investors often use is to look for companies with an ROE that is in line with or slightly higher than the industry average.
How to Calculate ROE
Calculating ROE is quite simple, namely by dividing net profit by shareholder equity:
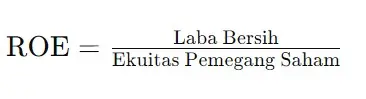
Net profit is the difference between net income and all costs, including interest and taxes. Shareholders' equity is the total capital invested by shareholders, after deducting debt.
A higher ROE indicates the company is more efficient at generating profits from invested capital.
Example of Using ROE
Return on Equity (ROE) is not just a number that shows how well a company performs. But this metric can also be used as a tool to project the future growth of a stock and analyze possible risks.
Investors can use ROE to estimate stock growth rates. This is assuming that the ratio is in line with or slightly above the average of the company's peer group. The following are examples of its use:
Estimating Future Growth Rates
One way investors use ROE is to estimate the future growth rate of a company, including the growth of dividends that will be paid.
To estimate this growth rate, investors can multiply the ROE by the company's retention ratio.
The retention ratio is the percentage of net profits that a company retains or reinvests to fund future growth, rather than distributing it as dividends to shareholders.
For example, if a company has an ROE of 15% and a retention ratio of 70%, then the sustainable growth rate (SGR) can be calculated using the following formula:
SGR = ROE × Retention Ratio
In this example, the sustainable growth rate for the company is:
15% × 70% = 10,5%
Another company may have the same ROE of 15% but have a retention ratio of 90%, meaning their sustainable growth rate will be higher, namely:
15% × 90% = 13,5%
This difference in growth rates can tell investors about a company's future growth potential without having to borrow additional funds.
Identifying Risks Using ROE
While a high ROE can be a positive sign, it can also indicate certain risks if not analyzed properly.
A very high ROE can be caused by a very large net profit compared to equity. However, it can also be a sign of problems such as low equity due to excessive debt or inconsistent profits.
Inconsistent Profits
One risk to pay attention to is inconsistent profits. Imagine a company called PT Index, which for several years has experienced losses and recorded negative values in shareholder equity.
However, if PT Index suddenly recorded a large profit again in the last year, the ROE calculation could become very high. But this does not reflect stable performance.
Excessive Debt
Another risk that can cause a high ROE is excessive debt. If a company borrows a lot of funds, this can reduce equity and artificially increase ROE.
This situation often occurs when a company borrows to buy back its own shares. This may increase earnings per share (EPS) but does not reflect actual performance or growth.
Negative Net Profit
Lastly, negative net income and negative shareholder equity can create an artificially high ROE. However, if a company records a net loss or negative shareholder equity, ROE should not be calculated as it does not provide a true picture of the company's performance.
In certain situations, companies that are actively buying back shares may have a negative ROE, but this is rare. In general, companies with negative ROE cannot be compared with other companies that have positive ROE.
By understanding the use of ROE in a broader context, investors can assess company performance more comprehensively and make more informed investment decisions.
What is the Difference between ROE and ROIC?
Although ROE and ROIC are often compared, they measure slightly different aspects of a company's financial performance. ROE measures how well a company uses shareholder equity to generate profits.
Meanwhile, Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) calculates the profit generated from all sources of capital owned by the company, including equity and debt.
In other words, ROIC provides a more comprehensive picture of a company's efficiency in utilizing the total capital it has to generate profits.
Conclusion
ROE is a very useful tool for investors to assess how efficient a company is at generating profits from shareholder capital. However, it is important to understand the context in which ROE is used and how it compares to other metrics such as ROIC.
This is to get a more comprehensive picture of the company's financial performance. By understanding the difference between ROE and ROIC, investors can make smarter and more informed decisions when investing in the stock market.
This is the discussion regarding ROE that we have summarized from various sources. Hopefully it's useful, OK!
How to Buy Crypto on Bittime
You can buy and sell crypto assets easily and safely via Bittime. Bittime is one of the best crypto applications in Indonesia which is officially registered with Bappebti.
To be able to buy crypto assets on Bittime, make sure you have registered and completed identity verification. Apart from that, also ensure you have sufficient balance by depositing some funds into your wallet. For your information, the minimum purchase of assets on Bittime is IDR 10,000. After that, you can purchase crypto assets in the application. Study Complete Guide How to Buy Crypto on Bittime.
Monitor graphic movement of Bitcoin (BTC) price, Ethereum (ETH), Solana (SOL), and other cryptos to find out today's crypto market trends in real-time on Bittime.
Disclaimer: The views expressed belong exclusively to the author and do not reflect the views of this platform. This platform and its affiliates disclaim any responsibility for the accuracy or suitability of the information provided. It is for informational purposes only and not intended as financial or investment advice.



